Use the back button in your browser to exit from a program. This page is still under construction and the programs are living in two different places. Let me know if you have any issues.
| Number | Description |
|---|---|
| Chapter 1: Harmonic Oscillation | |
| 1-1 | The connection between harmonic motion and uniform circular motion. |
| 1-2 | Multiplication in the complex plane. Move the complex number z around in the complex plane with the arrow keys. |
| Chapter 2: Forced Oscillation and Resonance | |
| 2-1 | A damped forced harmonic oscillator with one degree of freedom. |
| Chapter 3: Normal Modes | |
| 3-1 | Two coupled pendulums. |
| Chapter 4: Symmetries | |
| 4-1 | Beats in two coupled pendulums. |
| 4-2 | Modes of the hacksaw oscillator. |
| Chapter 5: Waves | |
| 5-1 | Standing waves in a system of coupled pendulums with fixed ends. |
| 5-2 | Standing waves on a beaded string with fixed ends. |
| 5-3 | Standing waves on a beaded string with one free end. |
| Chapter 6: Continuum Limit and Fourier Series | |
| 6-1 | Normal modes of the continuous string with fixed ends, with k = nπ/L for n = 1 to ∞. The up and down arrow keys increase n. |
| 6-2 | Normal modes of the continuous string with one fixed end and one free end, with k = nπ/L ‐ π/2L for n = 1 to ∞. The up and down arrow keys increase n. |
| 6-3 | The Fourier series for the function of (6.19)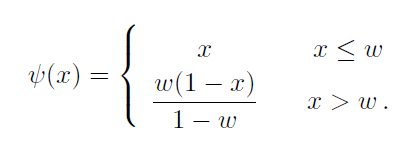 |
| 6-4 | Plucking an ideal string. |
| 6-5 | Same program as 6-4, but with variable inputs. |
| Chapter 7: Longitudinal Oscillations and Sound | |
| 7-1 | Longitudinal modes of a continuous spring with fixed ends. |
| 7-2 | Longitudinal modes of a continuous spring with one fixed end and one free end. |
| Chapter 8: Traveling Waves | |
| 8-1 | A traveling wave with a circle moving along the maximum of the wave at the phase velocity. |
| 8-2 | A traveling wave built out of two standing waves. |
| 8-3 | A traveling wave with damping. It peters out as it travels. |
| 8-4 | A forced oscillation problem for a continuous string with damping and one end fixed. |
| 8-5 | A forced oscillation problem for a beaded string with damping and one end fixed. |
| 8-6 | High- and low-frequency cut-offs in a forced oscillation problem. |
| Chapter 9: The Boundary at Infinity | |
| 9-1 | Looking at reflected waves. You can see the uneven motion of a traveling wave with a small reflected amplitude. |
| 9-2 | Reflection and transmission from a mass on a string. |
| Chapter 10: Signals and Fourier Analysis | |
| 10-1 | A triangular pulse propagating on a stretched string. |
| 10-2 | Group velocity (sum of two cosines). |
| 10-3 | Scattering of a pulse by a boundary between regions of different k. |
| 10-4 | Scattering of a pulse by a mass on a string. |
| Chapter 11: Two and Three Dimensions | |
| 11-1 | The modes of a two-dimensional beaded string. |
| 11-2 | Snell’s law with no reflection. |
| 11-3 | Water sloshing in a rectangular container. |
| 11-4 | Two immiscible liquids sloshing. Note the mismatch between the upper and lower liquids in the middle. This is the result of the nonlinearity of the constraint of incompressibility. |
| Chapter 12: Polarization | |
| 12-1 | Polarization in the two-dimensional harmonic oscillator, or in an electromagnetic wave. This shows the position of a string stretched in the z direction. The transverse position is shown in the x-y plane along with the x and y components. Alternatively, this can represent Ex and Ey in the electromagnetic wave propagating in the z direction and the total E field. In the upper left-hand corner is the complex two dimensional vector, that describes the polarization. You can change u1 between 1 and 0 with the left and right arrows. You can change |u2| between 1 and 0 with the up and down arrows. F1 and F2 decrease and increase the phase of u2 between π and -π. |
| 12-2 | The wandering of the electric field in unpolarized light. The electric field direction in the x-y plane is indicated by the trace. The color of the line changes occasionally to make it visible. |
| Extra Special Bonus Programs | |
| Rainbow | Demonstration of red and blue light refracting in a raindrop. |
| Rainbow 2 | Visualization of the double rainbow and Alexander’s dark band. |
| Water20 | Water waves in an infinite ocean. |
| Lens | Light refracting through a lens. |
| X-ray | The relationship between color and phase in x-ray diffraction. |
| X-ray 2 | A demonstration of x-rays diffracting through a crystal. |
| Purcell | The electric field generated by a particle that starts moving. |
| Purcell 2 | The electric field generated by a particle that stops moving. |
| Chladni plates | The vibrational modes of a chladni plate. |
| Accelerometer spring | MOBILE ONLY– lock your phone in portrait mode for best results. Displays a mass on a spring that you can control using your phone’s accelerometer. |
This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 4.0